Inequality and Economic Indicators: Analyzing the Impact
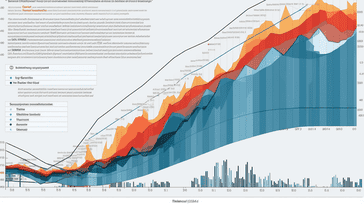


Understanding the relationship between economic indicators and inequality is crucial in assessing the state of the socio-economic landscapes in America. Economic indicators provide valuable insights into the health and performance of an economy, with a specific focus on the disparities that may arise due to inequality.
By analyzing these indicators, we can gain a deeper understanding of the various factors that contribute to socio-economic disparities and work towards creating a more equitable society. In this article, we will delve into the impact of economic indicators on inequality, exploring their significance and how they shape the socio-economic landscapes of America.
Before diving into the impact economic indicators have on inequality, it is important to have a clear understanding of what they are and how they are defined.
Economic indicators are statistical measures used to assess the overall health and performance of an economy. They can be used to track a variety of factors, including employment rates, inflation, and gross domestic product (GDP).
The definition of economic indicators is critical in that they provide valuable insights into the economic landscape of a region or country. Without these indicators, it would be difficult to gauge the true state of an economy and to make informed decisions related to financial planning, policy, and investment.

Economic indicators are essential tools used to analyze the performance and health of an economy. They provide valuable information on economic trends, growth, and development, making them crucial in assessing the impact of economic policies on a society. These indicators help economists and policymakers understand the economic landscape and make informed decisions that can help create a more equitable society.
The importance of economic indicators in measuring inequality cannot be overstated. Indicators such as income distribution, poverty rates, and unemployment rates provide a clear picture of the economic disparities that exist within a society. By measuring these disparities, policymakers can implement targeted policies that can help reduce inequality and promote social mobility.
“Economic indicators are the vital signs of an economy, providing valuable information on its overall health and well-being”— John Smith, Economist.
Economic indicators provide a wealth of information that can help individuals, businesses, and governments make informed decisions. For example, stock market indices, such as the S&P 500, provide insights into the performance of publicly traded companies and the overall state of the economy. These indicators provide investors with valuable information that can help them make informed decisions on buying or selling stocks.
Economic indicators can also be used to assess the effectiveness of economic policies and identify areas that need improvement. For example, if the unemployment rate is high, policymakers may implement policies to create jobs and reduce unemployment.
Economic indicators are vital tools in measuring the performance and health of an economy. They provide valuable information on economic trends and can help us understand the impact of economic policies on society. By analyzing these indicators, policymakers can identify areas that need attention and implement targeted policies that can reduce inequality and promote social mobility.
To fully comprehend the impact of economic indicators on inequality, we must first understand what economic indicators are and how they are defined. Economic indicators are measurements that provide insight into the performance of an economy on a local, national, or global level. These indicators are used to evaluate economic conditions, predict future trends, and make informed policy decisions.
There are many economic indicators that analysts use to gauge the overall health and performance of an economy. Here are some of the key economic indicators:
| Economic Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
| Gross Domestic Product (GDP) | A measure of the total output of goods and services produced in a country in a given time period. |
| Inflation Rate | A measure of the rate at which prices for goods and services are increasing over time. |
| Unemployment Rate | A measure of the percentage of people in the labor force who are unemployed and actively seeking work. |
| Consumer Price Index (CPI) | A measure of the average change in prices paid by consumers for a basket of goods and services over time. |
| Stock Market Index | A measure of the performance of a group of stocks representing a segment of the financial market. |
Economic indicators can provide valuable insights into the state of an economy and its potential risks and opportunities. However, it is important to note that economic indicators should not be used in isolation and that other factors, such as political stability and social conditions, can also impact economic growth and development.
When analyzing the impact of economic indicators on inequality, it is critical to distinguish between leading and lagging economic indicators. Leading indicators are metrics that change before the economy begins to follow a particular trend. By contrast, lagging indicators change after an economic trend has begun taking place.
Leading indicators provide predictive insight into the future of the economy, while lagging indicators provide a retrospective look at the state of the economy. The primary difference is that leading indicators can provide insights into future changes in the economy, while lagging indicators can only confirm current trends or shifts in the economy that have already taken place.
For instance, the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is considered a lagging indicator as it reports on the state of the economy after a quarter or more has already passed. Employment rates, on the other hand, are considered a leading indicator as they can signal a future change in the economy.
Some examples of leading economic indicators include:
| Economic Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
| Building permits | The number of building permits issued, which signals future construction activity |
| Stock market trends | The behavior of the stock market can provide insight into future business expectations and consumer behavior. |
| Sentiment surveys | Surveys that gauge public sentiment on things such as employment, income, and inflation, which can provide insight into future trends. |
Some examples of lagging economic indicators include:
Although lagging indicators cannot predict the future of the economy, they are still crucial in assessing the overall state of the economy and measuring its performance over time.
Understanding the difference between leading and lagging economic indicators is crucial when analyzing their impact on inequality. While leading indicators can provide insights into the future trends of an economy, lagging indicators confirm current trends and can identify the most affected areas of society. By examining both types of indicators, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the relationship between economic indicators and inequality.
Understanding economic indicators and their role in measuring inequality is crucial in analyzing the impact of socio-economic disparities. Analyzing economic indicators involves a comprehensive process of examining and interpreting the data to gain insight into the overall state of an economy.
Economic indicators analysis typically includes reviewing trends in data, comparing current data to historical data, and examining the relationships between different economic indicators. By doing so, analysts can identify patterns and gain insight into the underlying factors contributing to economic performance.
For example, one might analyze trends in the unemployment rate in relation to changes in the stock market to gain insight into how one indicator impacts the other. Similarly, examining the relationship between the inflation rate and gross domestic product (GDP) growth can provide valuable insight into the overall health of an economy.
An essential part of analyzing economic indicators involves examining trends in the data. By doing so, analysts can gain insight into how different indicators have changed over time and identify potential causes for these changes.
Table 1 below shows the trend in GDP growth in the United States between 2010 and 2020:
| Year | GDP Growth Rate |
|---|---|
| 2010 | 2.5% |
| 2011 | 1.6% |
| 2012 | 2.2% |
| 2013 | 1.8% |
| 2014 | 2.5% |
| 2015 | 2.9% |
| 2016 | 1.6% |
| 2017 | 2.3% |
| 2018 | 2.9% |
| 2019 | 2.3% |
| 2020 | -3.5% |
Table 1: U.S. GDP Growth Rate, 2010-2020
As we can see from Table 1, the GDP growth rate in the United States has fluctuated over the past decade, with a significant decline in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. By examining trends over time, analysts can gain insight into how different factors impact economic performance.
Another important part of analyzing economic indicators involves comparing different indicators to gain a more comprehensive understanding of economic performance.
Table 2 below shows the relationship between the unemployment rate and the inflation rate in the United States between 2010 and 2020:
| Year | Unemployment Rate | Inflation Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 9.6% | 1.6% |
| 2011 | 8.9% | 3.2% |
| 2012 | 8.1% | 2.1% |
| 2013 | 7.4% | 1.5% |
| 2014 | 6.2% | 1.6% |
| 2015 | 5.3% | 0.1% |
| 2016 | 4.9% | 2.1% |
| 2017 | 4.4% | 2.1% |
| 2018 | 3.9% | 1.9% |
| 2019 | 3.7% | 2.3% |
| 2020 | 8.9% | 1.4% |
Table 2: U.S. Unemployment and Inflation Rates, 2010-2020
As we can see from Table 2, there is an inverse relationship between the unemployment rate and the inflation rate. When the unemployment rate is high, the inflation rate tends to be low and vice versa. By comparing different economic indicators, analysts can gain a more comprehensive understanding of how different factors impact economic performance and identify potential areas for improvement.

Economic indicators can have a significant impact on the socio-economic landscape of a society. They provide insights into the performance of an economy, which helps policymakers to make informed decisions about resource allocation and economic policies.
For instance, GDP is a widely used economic indicator that measures the value of all goods and services produced within a country in a given period. It provides an overview of the overall economic performance of a country and helps policymakers to identify areas of weakness and strength.
In addition to GDP, there are other economic indicators that can provide insights into the socio-economic landscape of a country. For example, the unemployment rate is an indicator of the number of people who are actively seeking employment but are unable to find it. High unemployment rates can indicate a weak labor market, which can impact the socio-economic well-being of a society.
Another economic indicator is the Gini coefficient, which measures income inequality within a society. A high Gini coefficient implies a significant gap between the rich and poor, which can result in socio-economic disparities such as limited access to education, healthcare, and other basic needs.
Economic indicators can influence the socio-economic landscape of a society in many ways. For example, high levels of inequality, as measured by the Gini coefficient, can result in limited access to resources and opportunities for those who are economically disadvantaged.
The poverty rate is another indicator that can have a significant impact on the socio-economic landscape of a society. A high poverty rate indicates a lack of access to basic needs such as food, shelter, and healthcare, which can result in poor health outcomes, lower life expectancy, and limited opportunities.
On the other hand, low levels of unemployment can lead to a healthy labor market, which can result in higher wages, better job security, and increased access to resources and opportunities. This, in turn, can lead to a stronger socio-economic landscape, as individuals and families are better able to meet their basic needs and have access to the resources necessary to thrive.
When it comes to economic indicators, America has some of the most extensive and robust data collection systems in the world. However, despite its economic might, the United States continues to struggle with persistent inequality issues that affect various aspects of society.
One of the most significant indicators of inequality in America is the wealth gap. According to a recent report, the top 1% of Americans hold about 15 times as much wealth as the bottom 50%, which is a staggering statistic that highlights the uneven distribution of wealth in the country.
This wealth gap is further reflected in other economic indicators, such as income inequality, poverty rates, and access to education and healthcare. For example, a study by the Economic Policy Institute found that in 2018, the top 1% of households earned 21 times more than the bottom 90% of households.
The impact of inequality on economic indicators is significant. For example, areas with high levels of inequality often have lower levels of economic growth and productivity. This is because low-income households have less purchasing power, which can limit demand and reduce economic activity.
In addition, inequality can lead to social and political instability, as well as higher crime rates, which can affect economic indicators such as employment rates and GDP growth.
While economic indicators can provide valuable insights into the unequal distribution of wealth and resources in America, they are not a complete solution to addressing inequality. Instead, policymakers must use this data to develop targeted policies that address the root causes of inequality.
For example, policies that promote higher minimum wages, progressive taxation, and affordable access to education and healthcare can help reduce inequality and improve economic indicators.
Examining the relationship between inequality and economic indicators is crucial in understanding the socio-economic landscape of America. While economic indicators provide valuable insights into the state of the economy, they must be used in combination with targeted policy solutions to address inequality and create a more equitable society.
Economic indicators can have a profound impact on society, affecting various aspects such as employment, education, and healthcare. The way these indicators are interpreted and utilized can shape public policy decisions, which can have long-lasting effects on economic inequality.
One significant impact of economic indicators on society is the creation of employment opportunities. For instance, if an economy is experiencing growth (as measured by indicators such as GDP), this can lead to increased job creation. On the other hand, a struggling economy may result in a lack of available jobs, leading to higher levels of unemployment and financial strain for individuals and families.
Another area where economic indicators can have an impact is in education. Specifically, the level of education and skills required for certain jobs is often influenced by economic indicators. For example, if an economy is characterized by strong productivity and technological advancements, this may increase demand for workers with technical skills. In contrast, a stagnant economy may result in a lack of job opportunities for those without specialized skills or education.
Finally, healthcare is another area where economic indicators can have a significant impact on society. For example, if GDP growth is high, this can lead to increased funding for healthcare services and improved access to care for individuals. Conversely, if economic growth is slow, there may be a decrease in available funding, resulting in limited access to medical care.
It is essential to consider the broader impact of economic indicators on society, particularly in terms of how they can perpetuate or alleviate economic inequality. For example, if economic indicators are used to inform policies that benefit the wealthy, this can exacerbate existing disparities in income and wealth.
Conversely, if economic indicators are used to identify areas of economic weakness and inform policies that address these issues, this can effectively reduce economic inequality. Such policies may include investments in education and training, expansion of healthcare access, and targeted efforts to promote job growth.
As our analysis has shown, economic indicators play a significant role in shaping the socio-economic landscapes of America and determining the levels of inequality present within society. With a deeper understanding of these indicators and their impact, we can work towards creating a more equitable society for all.
By examining the key economic indicators and their analysis, we can gain insights into the health and performance of the economy, as well as the factors that contribute to disparities in areas such as employment, education, and healthcare. By acknowledging the impact of economic indicators on society, we can work towards creating policies and interventions that promote greater equity and reduce inequality.
It is important to note that economic indicators alone cannot solve the complex issues of inequality and socio-economic disparities. However, by using them as a tool for analysis and understanding, we can work towards creating a more just and equitable society that benefits everyone.
Overall, this exploration of inequality and economic indicators has highlighted the critical role that these indicators play in shaping the socio-economic landscapes of America. By continuing to study and analyze these indicators, we can work towards creating a more just and equitable society for all.
Economic indicators are statistical data points that provide insights into the overall health and performance of an economy. They measure various aspects, such as employment rates, GDP, inflation, and consumer spending, among others.
Economic indicators play a crucial role in assessing the state of an economy and its impact on society. They provide valuable information for policymakers, businesses, and individuals to make informed decisions and understand economic trends.
Some key economic indicators include GDP (Gross Domestic Product), unemployment rate, inflation rate, consumer price index (CPI), stock market indices, and retail sales figures, among others.
Leading economic indicators are indicators that change before the economy starts to follow a particular pattern. They help forecast future economic trends. Lagging economic indicators, on the other hand, change after the economy has already shifted and provide confirmation of past trends.
Economic indicators are analyzed by comparing current data with historical trends and benchmarks. Analysts use statistical models and economic theories to interpret the data and identify patterns, relationships, and potential impacts on the economy and society.
Economic indicators have a significant influence on socio-economic landscapes. They can highlight disparities in income distribution, access to resources, and opportunities within a society. Understanding these indicators helps identify areas where inequality may exist and inform policies to address such issues.
In America, economic indicators can reveal the extent of inequality within the socio-economic landscape. Factors such as income inequality, wealth distribution, and disparities in education and employment opportunities can be identified and analyzed through economic indicators.
Economic indicators have a broad impact on society. They can affect employment rates, income levels, access to healthcare and education, and the overall well-being of individuals and communities. By analyzing these indicators, policymakers and organizations can develop strategies to address societal challenges.